In the ever-evolving landscape of social media, a new paradigm is emerging—one that promises greater autonomy, privacy, and control for users. Welcome to the era of decentralized social platforms.
These platforms are challenging the status quo dominated by centralized giants like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
They offer an alternative vision, where users, not corporations, hold the reins of their digital identities and interactions.
Breaking Away from Centralization
For years, centralized social media platforms have been under fire for their lack of transparency, susceptibility to censorship, and exploitation of user data.
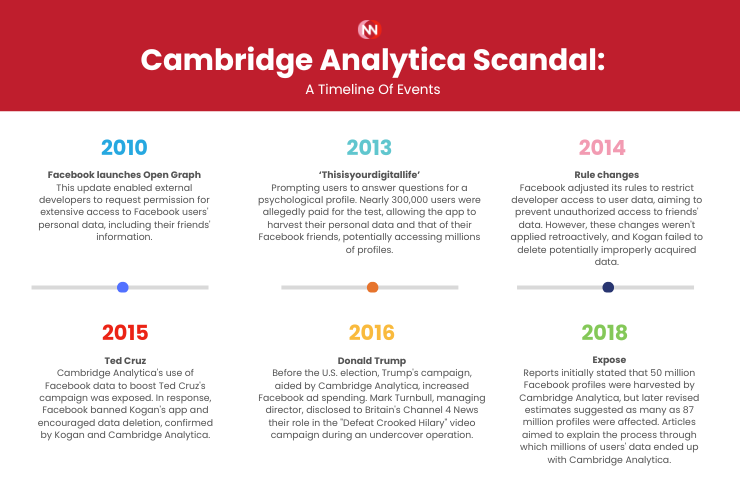
Events like the Cambridge Analytica scandal, where Facebook users' data was harvested without consent for political purposes, prompted widespread concern. Users began questioning the wisdom of entrusting their personal information to profit-driven corporations.
Decentralized social networks offer a remedy to these concerns by dispersing control away from a single authority. Instead of relying on a central server owned by a corporation, these networks operate on distributed networks, often utilizing blockchain technology. This decentralization not only bolsters security and privacy but also nurtures a more democratic and censorship-resistant environment.
 Giving Users Power
Giving Users Power
A fundamental tenet of decentralized social networks is user empowerment. These networks prioritize granting users ownership of their data and control over its dissemination.
Through methods such as cryptographic encryption and peer-to-peer networking, users can communicate directly without intermediaries.
Moreover, decentralized networks frequently incorporate token economies, rewarding users for their contributions with cryptocurrency. This encourages meaningful engagement and content creation while aligning users' interests with the platform's success.
Keeping Things Private
Decentralized networks act like personal lockboxes for user data, giving individuals the keys to control who accesses their information. Just as you safeguard valuables in your own lockbox rather than a shared safe, decentralized platforms prioritize user autonomy and privacy.
In the digital age, privacy has become a paramount concern, with mounting apprehension about surveillance, data breaches, and identity theft.
Decentralized social networks address these worries by design, minimizing the gathering and exposure of user data.
By leveraging encryption and decentralized storage, these networks ensure that sensitive information remains under the control of its rightful owners.
Users can interact and share content without apprehension of being tracked or targeted for advertisements.
.png)
Building a Diverse Community
Centralized social platforms often draw criticism for standardizing content and stifling diverse voices. Conversely, decentralized networks embrace diversity and inclusivity by design.
Without centralized gatekeepers dictating algorithms or content moderation, users enjoy the freedom to express themselves authentically.
Communities on decentralized networks are typically self-organizing, centered around shared interests or values rather than dictated by corporate algorithms. This grassroots approach nurtures genuine connections and cultivates a sense of belonging among users.
Decentralized networks, like a local farmer's market, empower users to directly exchange goods (content) without corporate middlemen. Both facilitate peer-to-peer transactions, fostering a more direct and community-driven exchange, free from centralized control and profit-seeking intermediaries.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their potential, decentralized social networks face challenges. User adoption remains a significant hurdle, as many are still unfamiliar with blockchain technology and wary of alternative platforms.
Additionally, scalability and usability issues must be addressed to compete with the seamless experiences offered by centralized incumbents.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and advancement. As awareness of privacy concerns and data sovereignty grows, more users may seek out decentralized alternatives.
With ongoing development and community backing, decentralized social networks have the potential to reshape how we connect and communicate online.
Both the shift to decentralized networks and the adoption of electric cars faced skepticism initially and required significant infrastructure changes. However, with growing awareness and technological advancements, both are gradually gaining traction and moving towards mainstream acceptance.
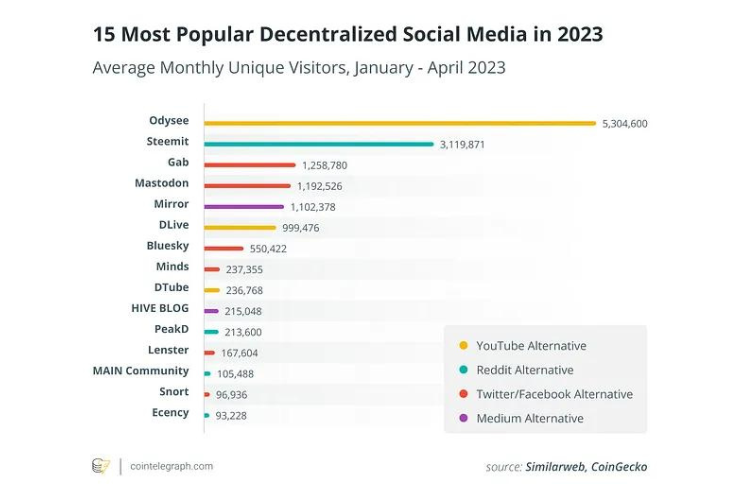
source: cointelegraph.com
Centralized vs Decentralized Social Networks
Centralized and decentralized social networks represent two contrasting approaches to how data is stored, managed, and distributed within a social network platform.
1. Centralized Social Networks
- Controlled by a single entity - In centralized networks, all user data, content, and functionality are managed and controlled by a central authority or company. Examples include Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
- Ease of use - Centralized networks often provide a seamless user experience due to the cohesive design and management by a single entity. Users typically sign up, create profiles, and interact within the network without needing to manage their data directly.
- Data ownership and privacy concerns - Users relinquish control of their data to the platform operator, raising concerns about privacy, data security, and potential misuse of personal information.
- Vulnerability to censorship and manipulation - Centralized networks can be subject to censorship, content moderation, and algorithmic manipulation by the controlling entity, which may impact the diversity of viewpoints and freedom of expression.
2. Decentralized Social Networks
- Distributed architecture - Decentralized networks distribute data across multiple nodes, often using blockchain or peer-to-peer technology. Examples include Mastodon (using ActivityPub protocol), Diaspora, and Secure Scuttlebutt.
- User control and ownership - In decentralized networks, users have greater control over their data and identities. They can choose where to store their data and which nodes to interact with, reducing reliance on a single centralized authority.
- Enhanced privacy and security - Decentralized networks often prioritize privacy and security by design, as data is not stored in a central repository vulnerable to hacking or surveillance.
- Resilience to censorship - Because there is no single point of control, decentralized networks are more resistant to censorship and manipulation. Information can flow freely among nodes, promoting a more diverse and open exchange of ideas.
Choosing between centralized and decentralized social networks often involves trade-offs between convenience, control, privacy, and security. Centralized networks may offer a more user-friendly experience but raise concerns about data privacy and censorship, while decentralized networks prioritize user control and privacy but may require more technical proficiency to use effectively.
Conclusion
The emergence of decentralized social media platforms, underpinned by blockchain technology, marks a significant shift in the social media landscape. These platforms prioritize user empowerment, data ownership, privacy, and freedom of expression.
They offer a solution to the limitations of centralized platforms by leveraging blockchain's transparency, security, and decentralized nature.
While challenges persist, the potential for a more user-centric, open, and inclusive social media experience is within reach. As awareness grows about the benefits of decentralized social media, the trajectory towards widespread adoption becomes clearer.
This signals an impending shift in the balance of power within the social media realm, tilting favorably towards the users.









You can choose to comment as a guest.